What Is UX Design
Have you ever used a website to do something, like book a vacation, and found the experience so easy and streamlined that it made you want to use that same website or app every time you go on vacation? Maybe the site was visually appealing, with incredible photos of your holiday options. And perhaps you found it so easy to pick the location and hotel that looked ideal, find the right dates, add extra activities, hire a car and book a whole package. If making the choices on the site, and moving through the screens and purchasing was pleasant and enjoyable, and enabled you to do what you needed to do, that’s because the site has great UX design.

What Is User Experience (UX)
You may have heard the term UX design a lot lately as digital products have become essential parts of our everyday lives. But you might be wondering exactly what UX design is and why it’s important. UX stands for User Experience, so UX Design is the process of designing functional digital products that people want to use. A lot of elements go into that process, but mainly a UX designer’s goal is to keep the user’s experience as the guiding principle to create products that are useful and easy to use.

Why Is UX Design Important
The user experience (UX) plays a crucial role in the success of digital products and services. UX refers to the overall interaction a user has with a product or system, including usability, accessibility, and overall satisfaction. In a hyper-competitive digital economy, with new digital products being released all the time, only the products that are easiest and most pleasant to use will gain traction with users. Companies have recognized that to have the best chance of success, focusing on excellent UX design is critical. And it is more than natural—anyone would prefer any everyday action, from shopping to getting jobs done as simple to perform as possible. If we get lost from the very first page of the website, it’s highly unlikely we will ever return there.
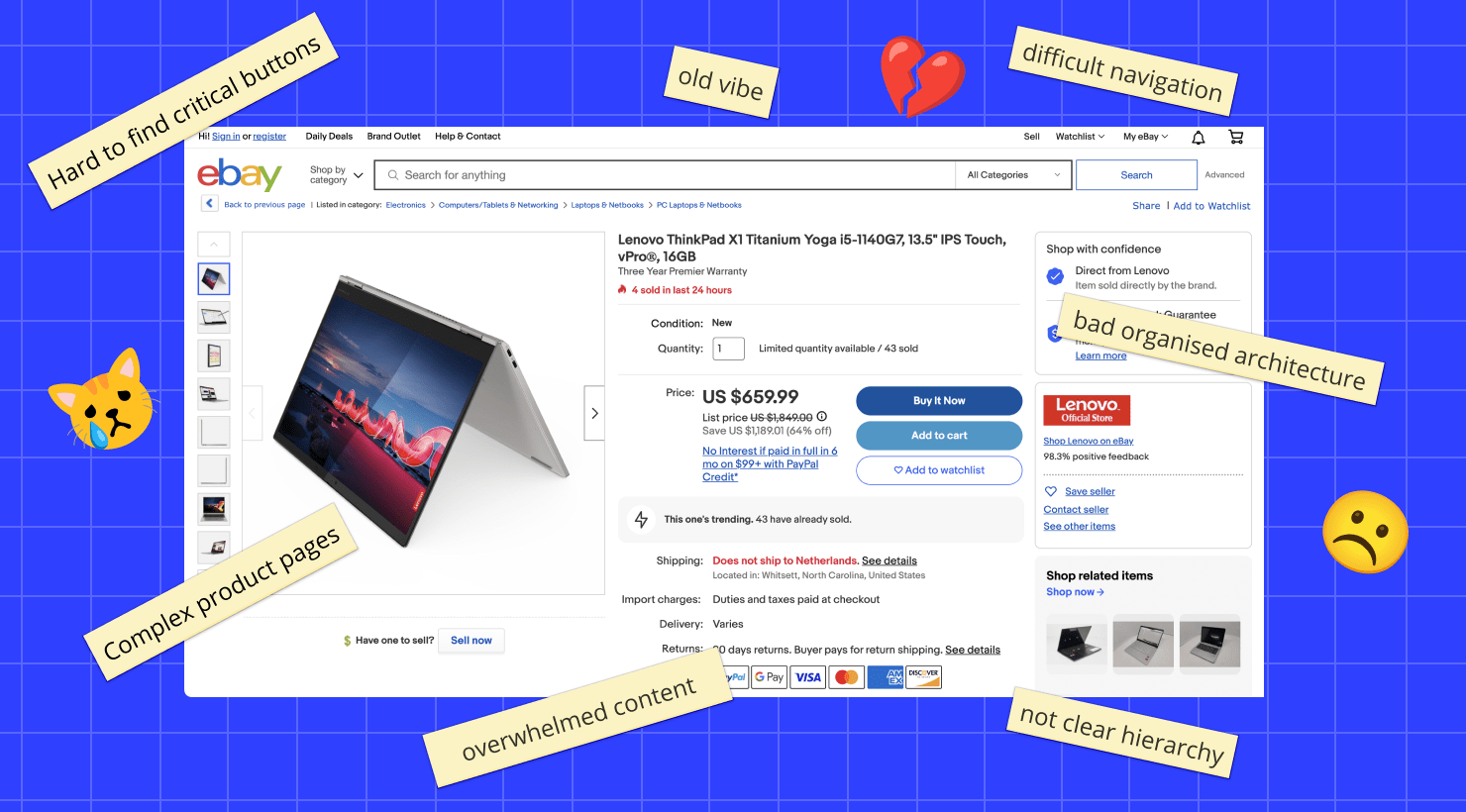
How Is UX Design Different From UI Design
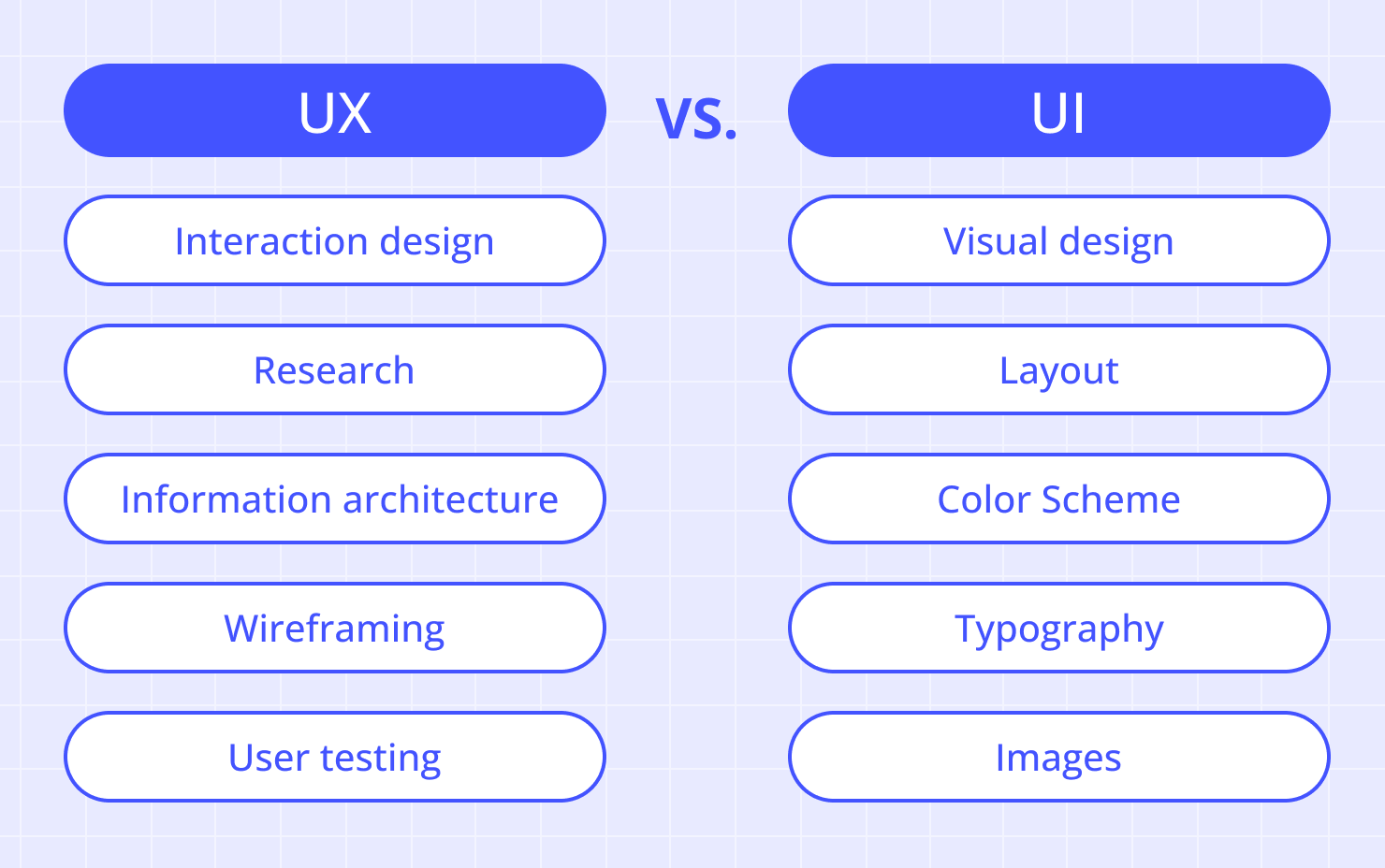
UX design and UI design are closely related as disciplines in the tech design world, but they are different. UX design is about the overall user experience of a product—from the time a user thinks about how a product meets their need, all the way through every interaction with the product. This field involves understanding what users want, and their behaviors and motivations. UX designers focus on user research, information architecture (how information is organized in an app or on a web page), interaction design, wireframing, prototyping and user testing.
By contrast, UI design doesn’t encompass the whole user experience. UI design is focused on the visual and interactive elements of a digital interface. The layout, colors, visual images and typography of an interface are the main things UI designers work with. They choose things like where buttons are placed, what will guide the user’s eye to the most important part of a page, and what color the navigation bar should be. Their aim is to make all visual interfaces of a brand appealing and consistent with the brand’s identity.
UX Design: An Official Definition
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the official organization that agrees on best practices and standards for different disciplines, officially defines UX design as:
“A person’s perceptions and responses that result from the use or anticipated use of a product, system, or service.”
As you can see from the definition, UX design doesn’t just consider things like tapping “add to cart” while using an app, but the users’ perceptions of using the app, how it makes them feel, and the way they respond to it.
If that sounds a lot like psychology, it’s because it really is! Why users behave the way they do is a central theme of UX design. And learning about behavior is psychological, so the entire UX discipline certainly overlaps with psychology.
UX Design in Digital Products
Most often, we use the term “UX” to apply to digital experiences today. In that context, User Experience is concerned with how a user feels when interacting with a website or app. The most important aspects of UX would be things like
- What encourages a user to want to download the app?
- Where will the user focus their eyes on the screens?
- How many choices does the user have from each screen to perform an action?
- How easy is it to move through the app?
- How many steps does it take for a user to perform each action?
- How can a user undo actions?
- How is a user notified they have made an error?
- How does the app make users feel when they are interacting with it?
- Do users return to the app frequently?
These aren’t all the elements of UX design, but they are major considerations when thinking about a user’s experience with an app or website. Need some inspiration for a beautiful UX through the years? Everyone knows exactly the company which has answered all of the above virtuously—from 1998 Google managed to grow into the most widespread search engine with over 3.5 billion searches every day and its UX is as straightforward as can be!
UX Design: More Than Digital Experiences
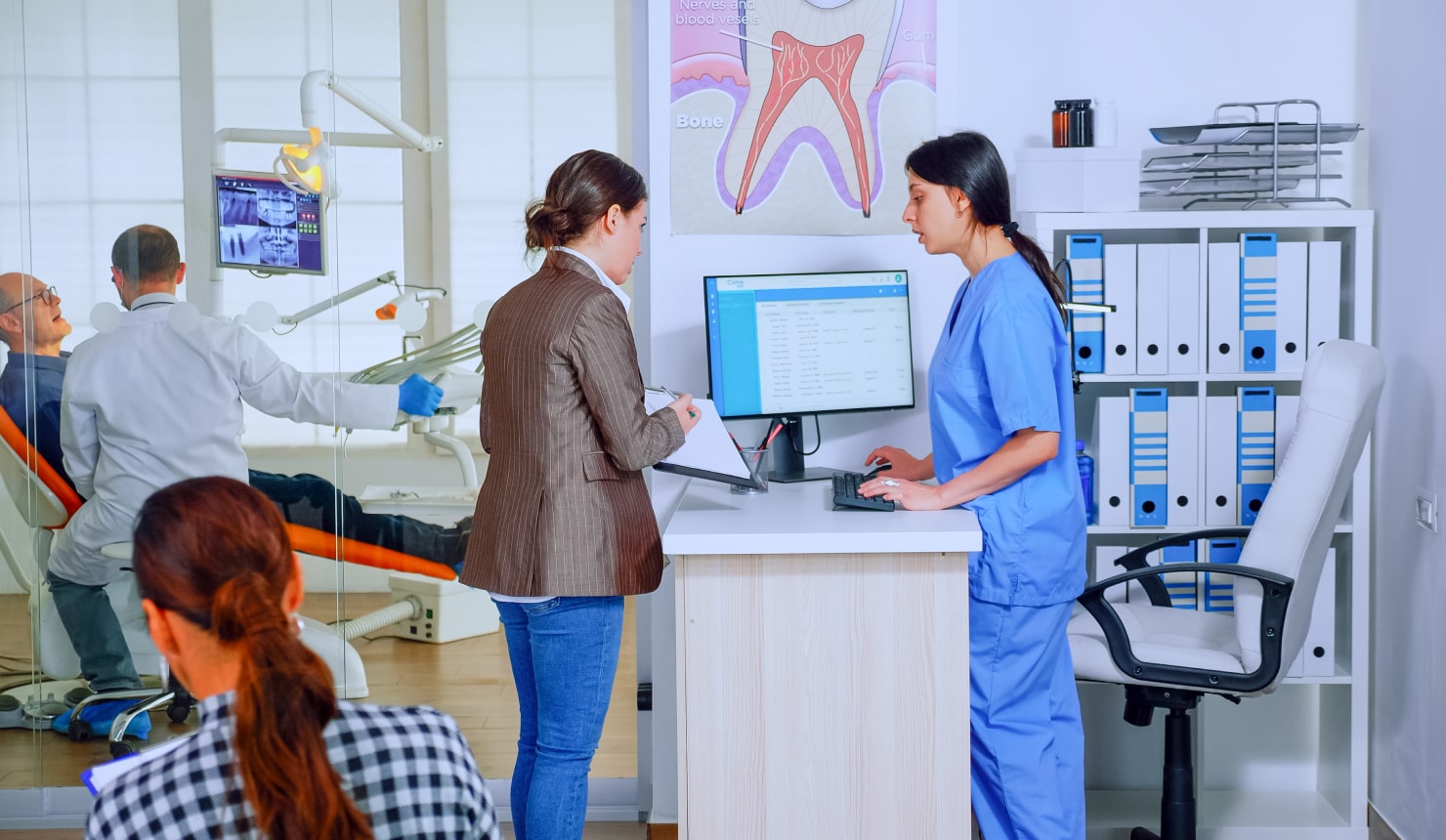
Actually, UX design can also apply to any product or service, not only digital products and apps we all use. UX design can apply to things like booking an appointment at the dentist. For example, the user experience here would consider things like: how easy it is to call an office to book, or are they able to book an appointment online? Then how does the user locate the dental office, and what is the experience of walking into the office and registering like? And how is the experience of waiting for an appointment, and how long does it take to be seen by the dentist? Then what is the appointment itself like? UX Design considers all aspects of the appointment, until the point the patient leaves the office. This is all part of the User Experience.

Principles of UX Design
As a UX designer, the main questions you’ll focus on are the why and how of a product or service. While the product team or the business team might define “what” you’ll be designing, the UX designer or team of designers will think about why the product is being created, and how it will serve users.
UX design involves keeping these important principles in mind to build a product that users will love:
- Usability
- Accessibility
- Desirability
- Utility
- Findability
- Credibility
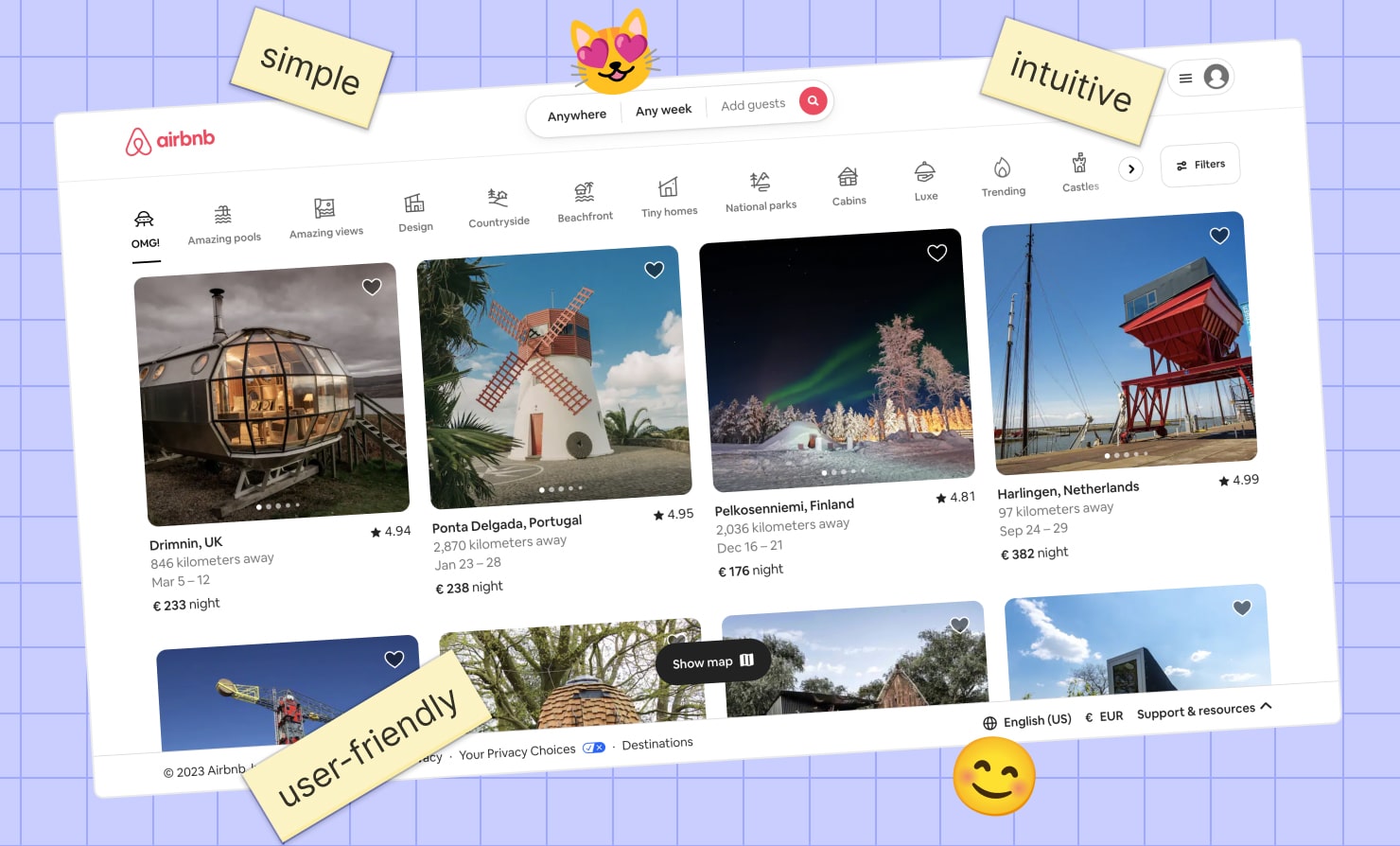
All these are easily found on the Airbnb website: simple yet versatile search, viewing prices on the map to get the whole picture, different help boxes like “you won’t be charged yet” or “this is a rare find”. Good example of following UX principles is having everything the user needs exactly when they need it.
How UX Designers Work
Most UX designers have general steps to follow when creating a product. Even though this process is different for different teams, generally all UX designers will go through similar steps to have a complete UX design process.
The general workflow for a UX Designer might look like this:
- User Research
- Conducting Surveys and Interviews
- Discovering User Behavior and Needs
- Information Architecture
- Organizing and Structuring Information
- Creating User Flows and Wireframes
- Interaction Design
- Designing User Interfaces
- Defining User Interactions and Gestures
- Prototyping and Testing
- Building Interactive Prototypes
- Conducting User Testing and Gathering Feedback
- Iteration and Improvement
- Incorporating User Feedback
- Refining and Enhancing the Design
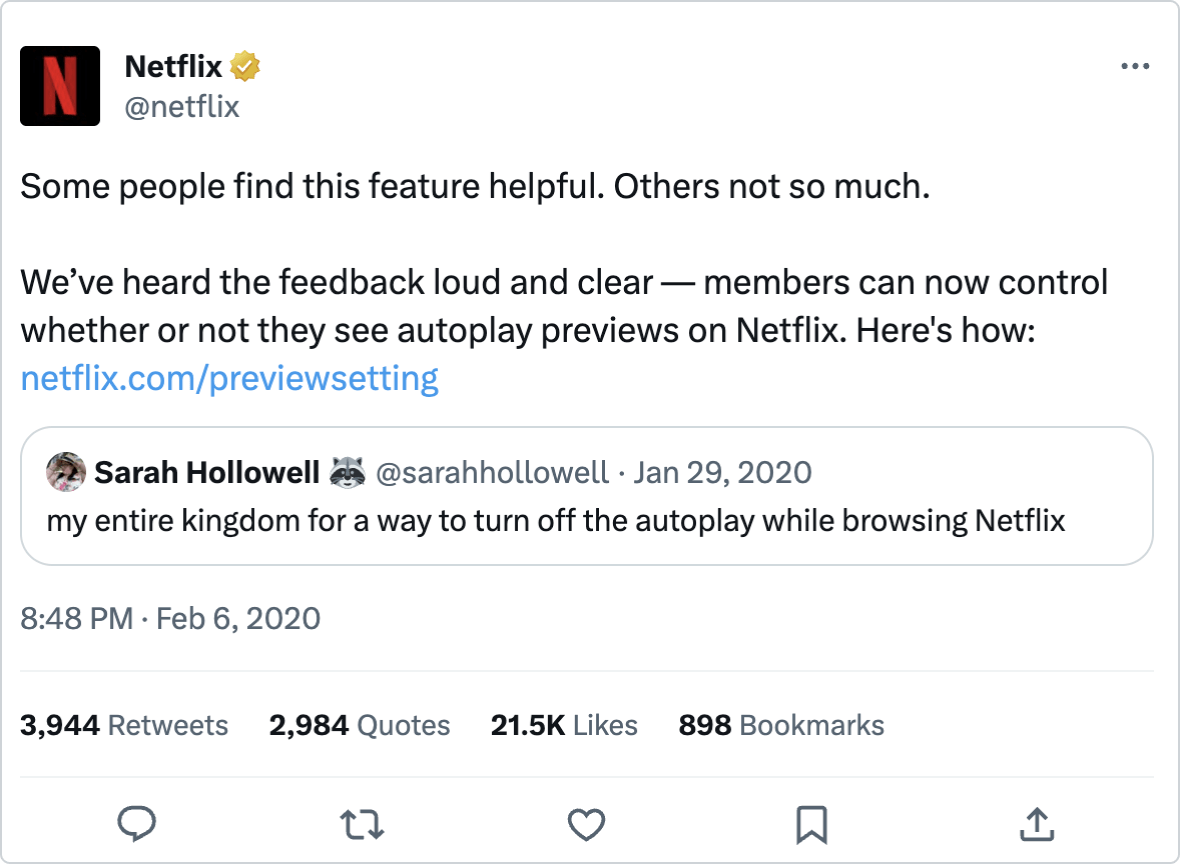
And never should a designer think that there’s a perfect UX without the user’s feedback! Even such giants as Netflix can sometimes bring the most annoying UX while seemingly offering the most useful of the features. Netflix introduced an autoplay trailer feature, which was instantly loved by some and deeply hated by others for its so-called “dark UX pattern”, so they had to offer the dissatisfied users the solution. So there’s the opportunity to learn to test the new features with users before the mass-release.
Important Skills for UX Designers
A lot of UX Designer’s work involves hard skills, like creating user flows (representations of how a user moves through an app) and wireframes (sketches of different screens), and designing a prototype. Some of these involve using software platforms and some involve simply sketching out ideas on a whiteboard.
But a UX designer also needs soft skills in addition to the hard skills above. Empathy for users is a must-have quality. UX Designers must be able to put themselves in the shoes of the user and understand their wants, needs and problems. It’s also important to have curiosity, and to be able to ask the right questions in order to create the optimal design for a product. Another key soft skill is communication. A UX designer has to communicate with teams across many functions. Often you’ll communicate with software developers, business owners, CEOs, product managers, and customers. It’s important to know how to communicate and speak to many different stakeholders to get valuable input for the design process.
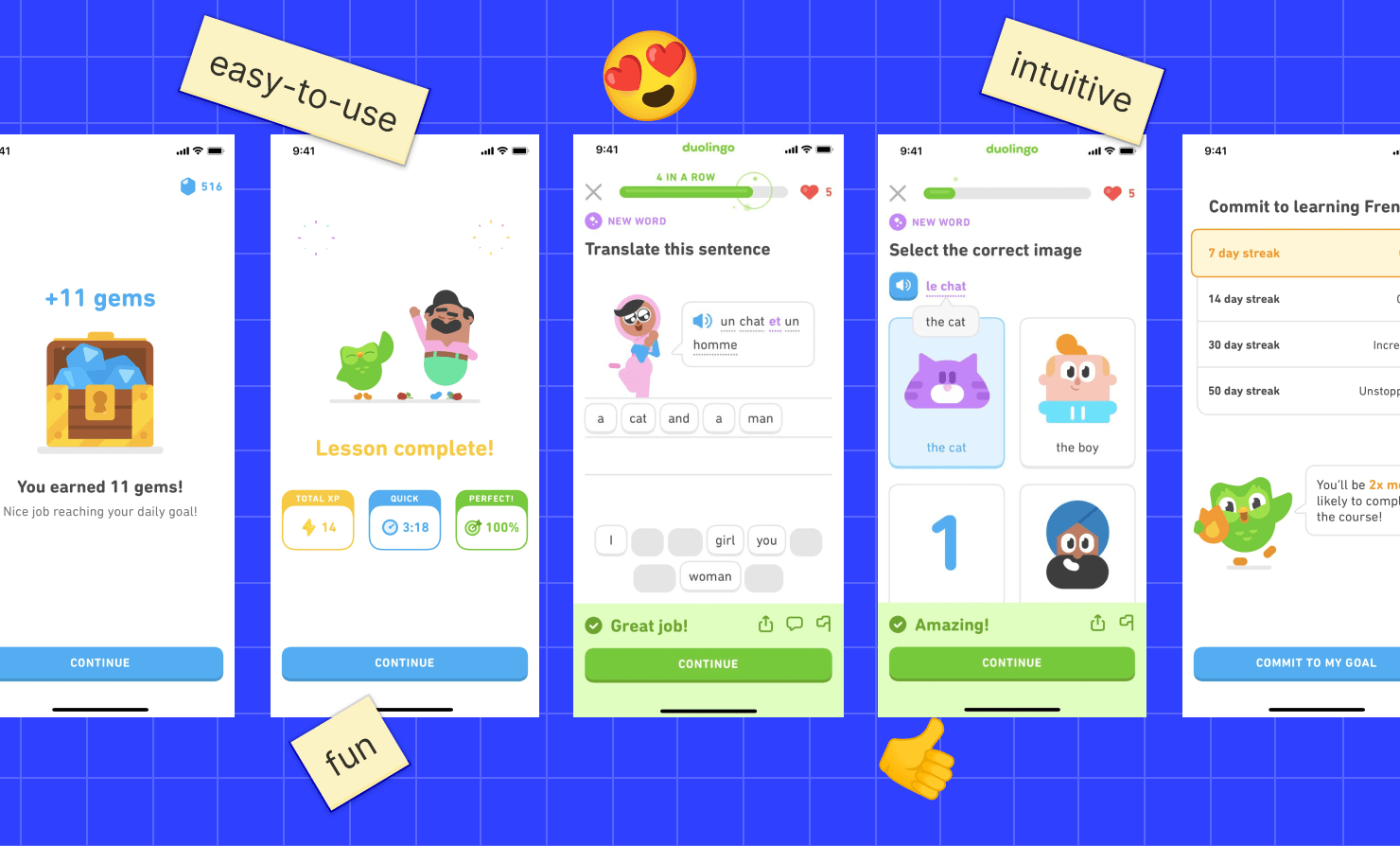
Arguably the most important skill though is the ability to relate to the users, as does Duolingo to challenge the users to return for more language knowledge. By including animations, a humorous tone of voice, and gamified UX features like levels, streaks, and more, they are able to make the process of learning a new language in a more engaging and fun way.
Software Used in UX Design
There are many software tools for a UX Designer to use to make their work easier and more collaborative. The most commonly used platforms in UX Design are:
- Figma: An online, collaborative tool for vector graphic editing and interface design.
- Adobe XD: A platform for designing experiences using vector-based tools.
- Maze: A platform that enables rapid user testing of UX prototypes, and gathers feedback from real users.
- Miro: A whiteboarding app for collaboration and sketching user flows
- Sketch: A collaborative digital design app for Mac users.
- InVision: A platform for designing digital products and creating prototypes.
- Webflow: A no-code website builder with a visual canvas for designing web experiences.
While not all these tools are essential to the UX design process, these are standard platforms that any UX designer might want to be familiar with to create a product.
Successful UX Design
At its core, UX design revolves around knowing and understanding users to craft a remarkable experience for them. If you want your product or business to succeed, it is essential to build a simple, easy and positive experience for your customers.
UX designers do this by prioritizing a user’s needs and expectations. The UX design process involves researching user behavior, uncovering needs, developing solutions, sketching screens and creating user flows. UX designers then create wireframes and develop a prototype. To finish the process, UX Designers test a product with users, and gather feedback to make changes and improve the product.
UX design involves many complex elements of behavior and design, but the goals of effective UX design are simple. Successful UX Design centers around creating a product that users will love and want to use again and again.