The Difference Between UX and UI Design
UX design and UI design are two central aspects of creating products, especially digital products. UX stands for “User Experience” and UI stands for “User Interface design.” While you may have heard of each of these, you might have assumed they were basically the same thing—a common misconception. This article will explain the difference between UX and UI design to give you a clearer idea of how each of these contribute to product creation. By the end of the article, you will see that while UX and UI design go hand in hand, they are quite different disciplines, with their own particular focus.
What Is UX Design?
In the realm of digital art and design, as well as physical product design, UX design is the part that shapes the user experience from start to finish. UX design focuses on understanding and enhancing the overall experience of users when interacting with a product or service. UX, or user experience, encompasses a range of tasks and responsibilities: user research, information architecture, interaction design, and prototyping.

Why Is UX Design Important?
The importance of UX design lies in its ability to create intuitive and meaningful experiences that delight users, increase engagement, and drive the success of products. Without understanding the user, their lives, problems, needs and wants, designers and business owners would simply create products that they themselves think would be helpful—but that no one else may actually use. User-centered design is critical to making a product that solves problems for the target audience.
What Does a UX Designer Do?
UX designers focus on empathizing with users. They are tasked with conducting user research and applying human-centered design to create products people love to use. In designing a product, UX designers begin with developing a strategy. This can involve competitor analysis, user analysis and research, product design and developing content. After this initial work, they begin to create basic visual representations of the product. This is sometimes referred to as product mapping, where designers lay out each stage of a user’s experience with a product. Designers can do this digitally, on a physical whiteboard, or even on paper.

Visual Design of a Product
Next UX designers begin creating wireframes, where they refine the product further. From this, they will create a prototype, which is an interactive model of the actual product. The prototype might look visually polished, but it is by no means the end of the process. The prototype is handed to developers who then create what has been designed. Once the first version of the product is launched, this is only the beginning point to find out whether it performs as expected.
Testing the Product
After the prototype has been developed, UX designers guide testing the product with users and collecting feedback from users on every aspect of usability. They will use the feedback to iterate on the product, then plan further development.
Iterating on the Product
During these stages of product development, UX designers track analytics to find out whether the product is hitting their goals. They will also coordinate with UI designers, developers and possibly product managers. This entire iterative process ensures that the product meets a user’s expectations and needs.
What Is UI Design?
User Interface (UI) design also is a key part of shaping our digital interactions. The difference between UX and UI design is that UI design focuses solely on the visual elements of a product or service. This covers everything the user will see or interact with: both with the layout and the functionality.
UI designers craft visually appealing interfaces that portray a consistent brand identity, and also blend into a seamless overall user experience. UI designers apply their skills to things like buttons, icons, font, typography and color palette. These details must all align with the goal of the product and aid in making it functional.
By combining visual design skills with a deep understanding of user needs, UI designers bring life to digital experiences that are visually compelling and easy to use.
Why Is UI Design Important?
The best UI design makes a product so easy to navigate that the user doesn’t have to think about how to do what they want to do. The goal of a UI designer is to lay out a visual experience that is clear and intuitive. The experience should also be visually consistent with the brand.
Perhaps you’ve opened an app on a mobile phone that didn’t adapt to the size of your phone. Maybe the page was still shown as if on a desktop screen, and you couldn’t even read the type. It’s likely that if this happened, you immediately left the app or web page. This is just one example of what can happen without a UI designer.
Without UI design in place, products can end up not being responsive across all devices. Interfaces can be hard to understand, or visually unappealing. And, it’s proven that users will abandon a product almost instantly if they are difficult to see or confusing to use. This leads to product market failure.
It is impossible to create an interface that is engaging and functional without in-depth knowledge and application of UI design principles. Great UI design is critical for user adoption and for making successful digital products.
What Are the Tasks of a UI Designer?
When you use a digital product or app, do you automatically think of the visual appeal? Maybe you naturally think about whether you would have chosen a different font, or whether you like the design of the user input boxes. If so, you’re thinking like a UI designer.
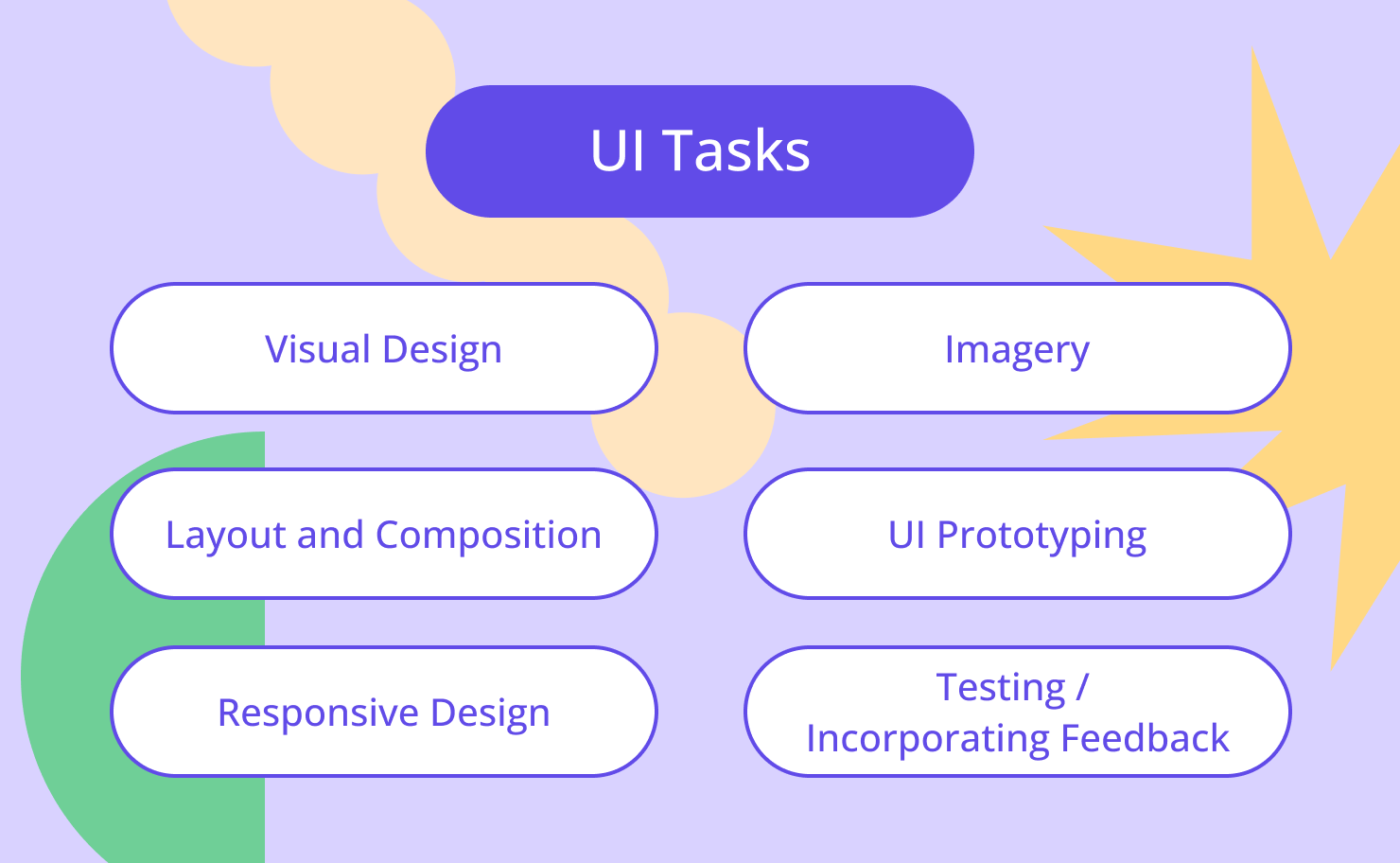
UI designers focus on taking the product specifications and turning those into something visually appealing and user-friendly. They perform a range of tasks, but here are some of the components a UI designers has to think about:
- Visual Design: Selecting typography, icons, imagery, and color, keeping in mind the brand identity and the target audience.
- Layout and Composition: Planning a clear visual hierarchy. Arranging navigation menus, buttons and content.
- Responsive Design: Adapting the interface design to different screen sizes and devices to ensure user experience is consistent across platforms and devices.
- Imagery: Selecting or creating icons and imagery to convey information and improve the user interface.
- UI Prototyping: Creating interactive prototypes or mockups to show how users will interact with the interface. This helps designers gather feedback, test usability, and validate decisions before development.
- Usability Testing and Incorporating Feedback: Participating in usability testing sessions to gather user feedback and insights. Based on feedback, designers refine the interface, and improve usability issues or pain points.
These are just a few of the responsibilities of UI designers. They also create style guides that create the standards for consistency among products across the company. These guides would include typography, the icon set, and selecting colors and UI components. A style guide helps ensure consistency for all designers and developers as they work on products and services.
How Do UX and UI Designers Work Together?
Collaboration and communication are key skills that UX and UI designers need in order to create a successful product. Both these teams regularly need to collaborate with other stakeholders in the business to make sure what they are creating meets the company’s goals. Open and regular communication between the business and the designers is important so designers understand the requirements and the rationale behind the product.
Collaboration with software developers and UX and UI teams is also important when designing digital products. These teams work together from the creation, launch and testing stages. As designers gather user feedback, they work closely with developers to iterate on the product based on feedback. Keeping close collaboration is the key to a successful product.

Conclusion
UX designers and UI designers each have important functions that are unique in focus and areas of specialization. But, both UX and UI design are critical to creating a successful product. These designers also need to work closely with the business stakeholders and with developers to make a product that meets their goals.
By empathizing with users, conducting thorough research, and applying design principles, UX designers create products that meet users’ needs and solve their problems. UI designers bring valuable skills and expertise to create visually engaging, attractive and user-friendly digital products. They ensure a product’s interface is so clear that users can navigate it successfully without much effort. Working together, UX designers and UI designers provide the foundation to create products that combine functionality with delightful user experience.